ARTICLE AD BOX
Introduced as a means to embed data within Bitcoin transactions, inscriptions—data or information embedded in a transaction that extends beyond the basic financial transaction details—extend the blockchain’s utility beyond financial exchanges. As of Dec. 18, the Bitcoin blockchain has witnessed the addition of approximately 47.36 million inscriptions, marking a notable development in its use.
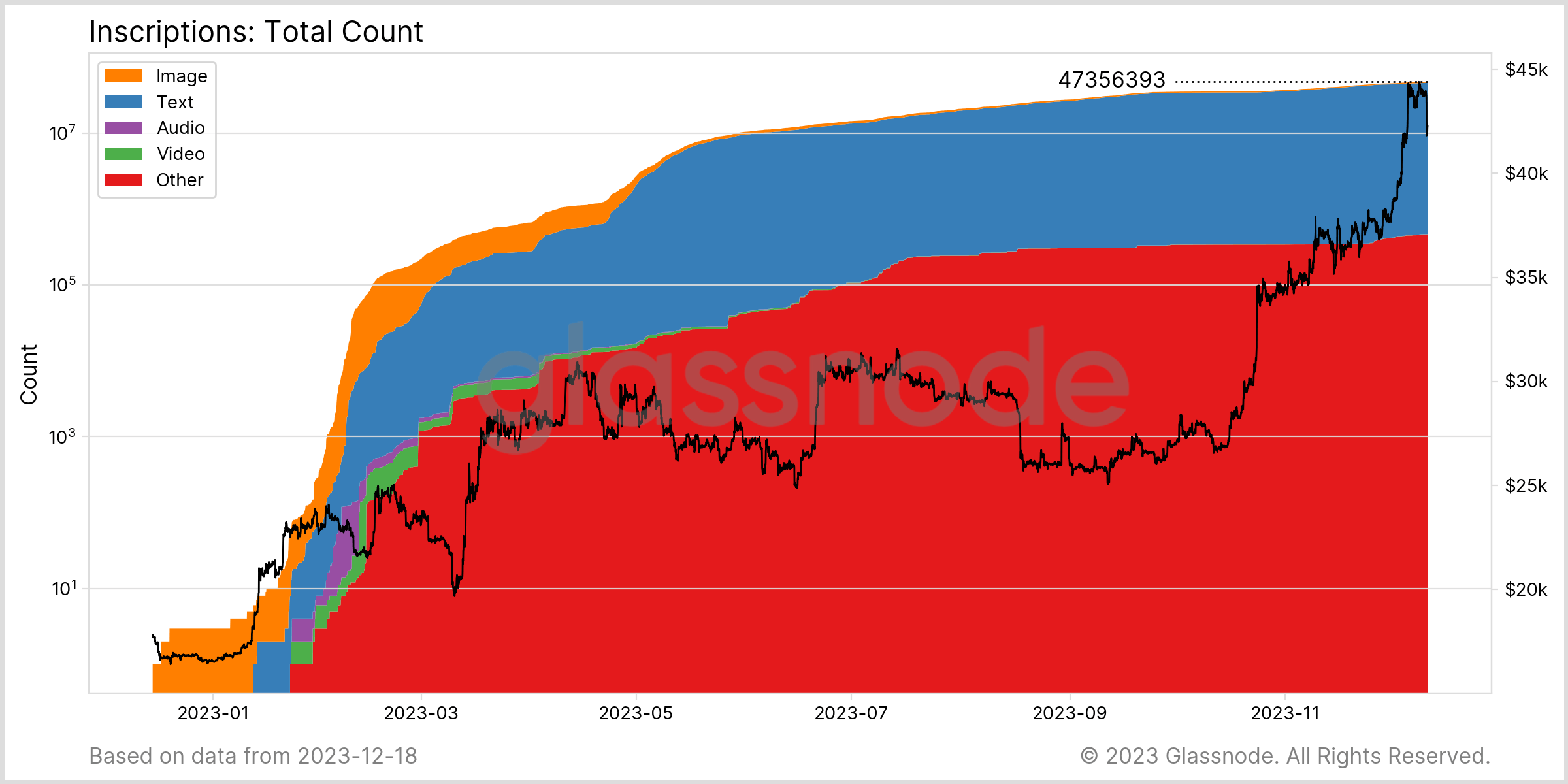 Graph showing the total number of inscriptions on Dec. 18, 2023 (Source: Glassnode)
Graph showing the total number of inscriptions on Dec. 18, 2023 (Source: Glassnode)Inscriptions are important because they represent a shift in how Bitcoin’s blockchain is utilized. Initially focused only on financial transactions, Bitcoin assumed new capabilities following the introduction of inscriptions.
This expansion, however, has not been universally welcomed. Critics of crypto industry argue that inscriptions consume excessive block space, leading to increased transaction fees and potentially rendering the network less accessible for standard financial transactions.
The nature of these inscriptions varies considerably. Text-based or BRC-20 inscriptions, which account for 96% of inscriptions at 45.48 million, are used for various purposes, from simple messaging to creating token standards on the Bitcoin network. In contrast, the 1.41 million image-based inscriptions often serve more complex functions than the NFTs seen in other blockchain ecosystems. Other categories, including audio and video inscriptions, contribute to the diversity but are relatively minor in terms of numbers.
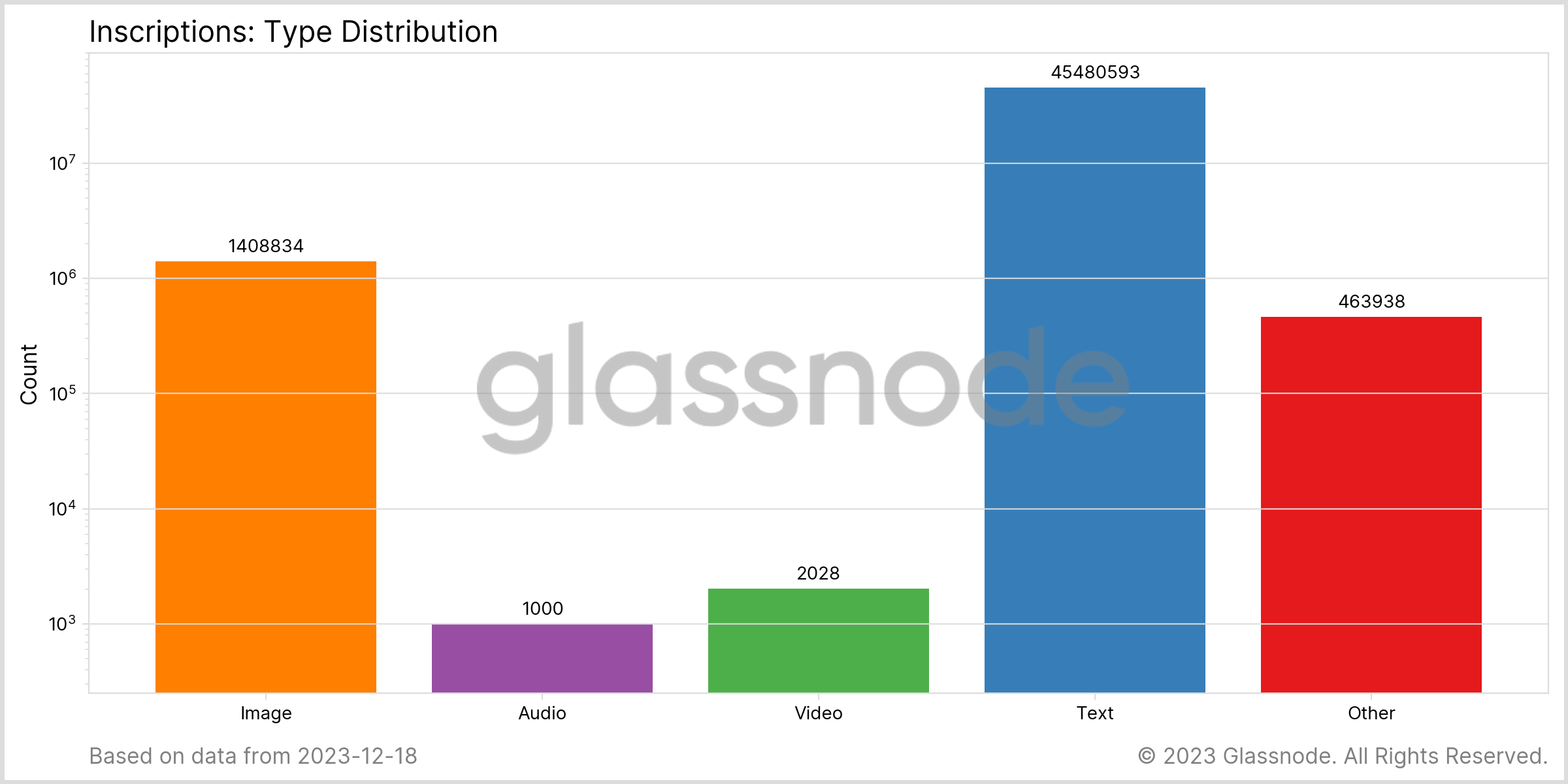 Chart showing the number of inscriptions by type (Source: Glassnode)
Chart showing the number of inscriptions by type (Source: Glassnode)The significance of these inscriptions extends beyond their sheer number to their size. Despite their numerical dominance, text-based inscriptions occupy only 3,234.6 MB of data. This pales compared to the 11,736 MB taken up by image-based inscriptions, highlighting a critical discrepancy between the number of inscriptions and their respective data footprint. This distinction is crucial because it directly affects the blockchain’s efficiency in handling data.
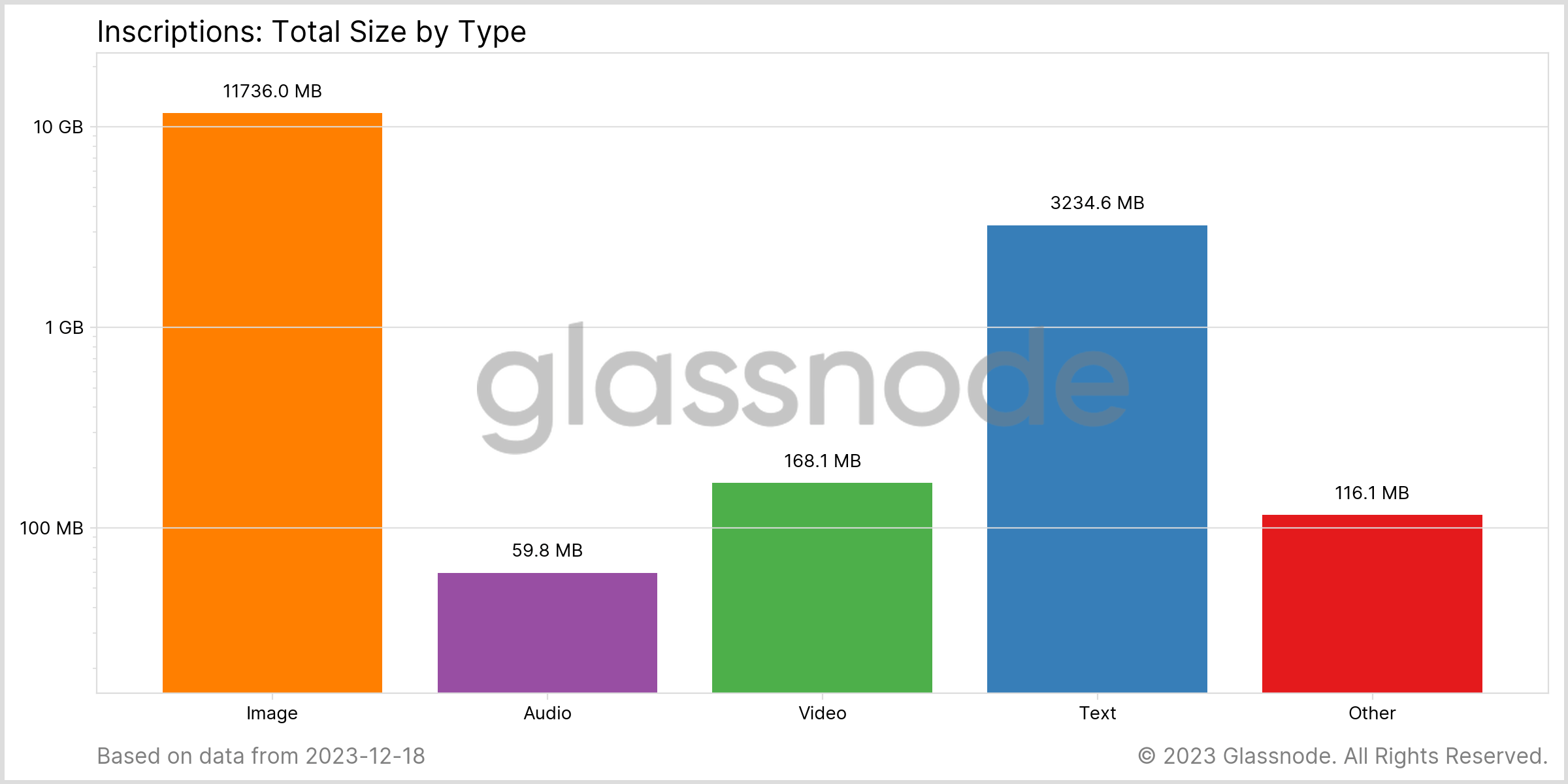 Chart showing the breakdown of inscription file size by file type (Source: Glassnode)
Chart showing the breakdown of inscription file size by file type (Source: Glassnode)The surge in inscriptions has had a tangible impact on Bitcoin’s transaction landscape. Throughout 2023, inscription-linked transactions consistently outnumbered standard financial transactions. On Dec.17 alone, there were 592,339 inscription transactions compared to 316,276 non-inscription transactions. This shift signifies a growing preference for using the Bitcoin blockchain for more than just monetary exchanges.
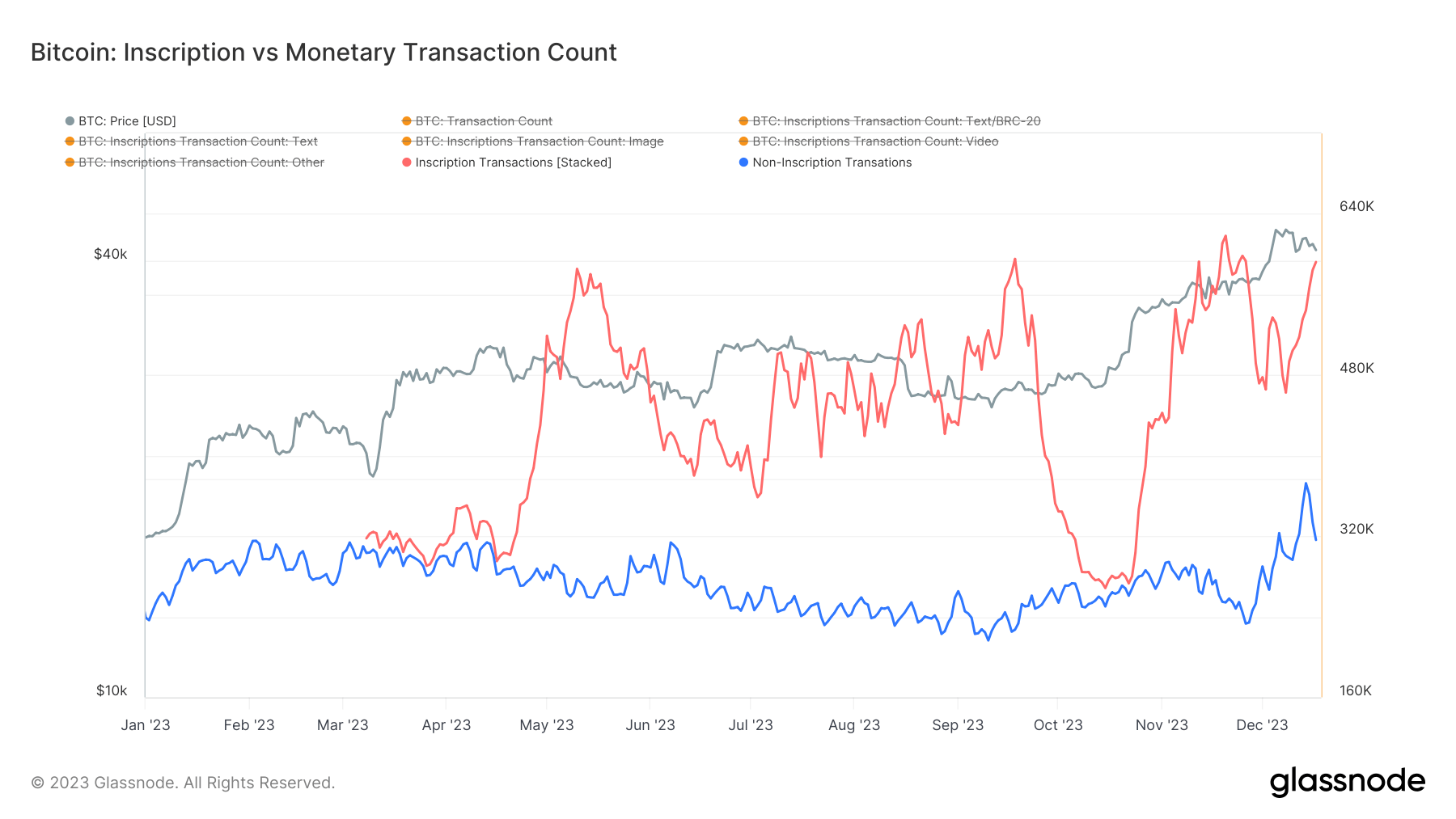 Chart comparing the number of inscription transactions (red) to the number of non-inscription transactions in 2023 (Source: Glassnode)
Chart comparing the number of inscription transactions (red) to the number of non-inscription transactions in 2023 (Source: Glassnode)The predominance of inscriptions, especially those with significant data sizes like images, raises concerns about the sustainability of the blockchain’s performance. High data volume inscriptions can increase block sizes, potentially causing network congestion and higher transaction fees. This situation poses a challenge for the Bitcoin network, balancing its traditional role as a financial ledger with its emerging function as a versatile data storage platform.
The adoption of inscriptions represents a pivotal moment in the blockchain’s history. While offering expanded utility, the widespread use of inscriptions, particularly large-sized ones, may have profound implications for the network’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness. As the blockchain continues to evolve, managing this balance between financial and data transactions will be crucial for maintaining Bitcoin’s functionality.
The post Beyond JPEGs: Exploring the types of Bitcoin inscriptions appeared first on CryptoSlate.
.png)
 1 year ago
7
1 year ago
7








 English (US)
English (US)